News
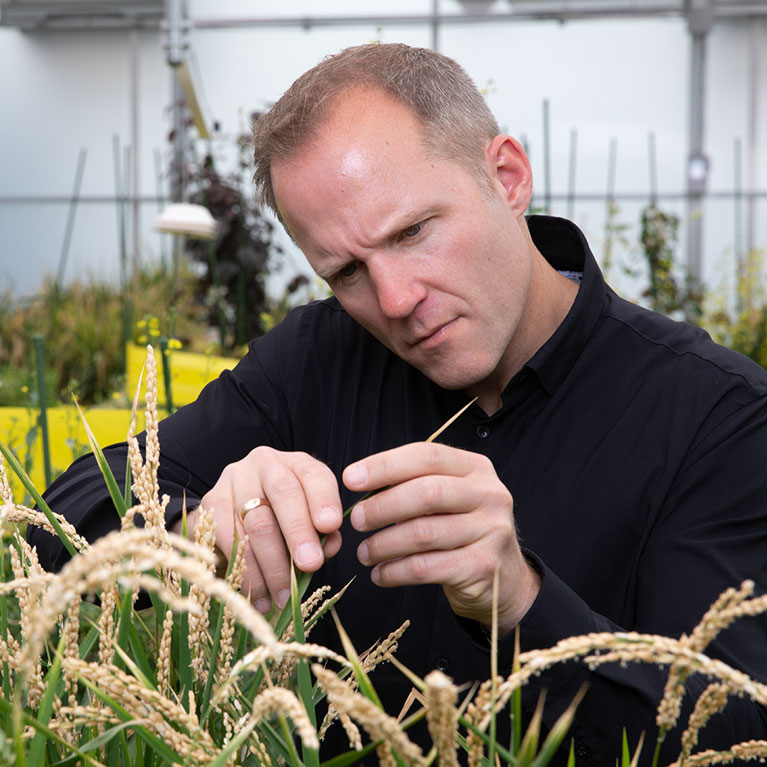
Salk Professor Wolfgang Busch receives NOMIS Distinguished Scientist and Scholar Award
LA JOLLA—Salk Institute Professor Wolfgang Busch, director of the Harnessing Plants Initiative and Hess Chair in Plant Science at Salk, has received a 2025 NOMIS Distinguished Scientist and Scholar Award. The NOMIS Foundation bestows this honor to “exceptional scientists and scholars whose innovative ideas and approaches involve interdisciplinary collaboration and apply a broad range of methods, building bridges across the boundaries of the sciences and humanities.”
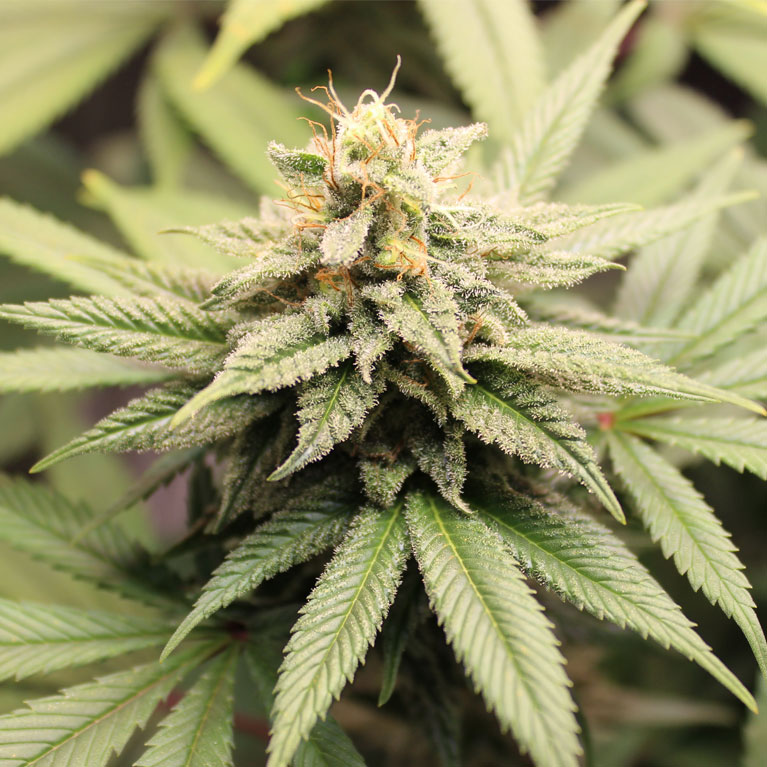
Cannabis pangenome reveals potential for medicinal and industrial use
LA JOLLA—Cannabis has been a globally important crop for millennia. While best known today as marijuana for its psychoactive cannabinoid THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), historically, cannabis has been a cornerstone of human civilization, providing seed oil, textiles, and food for more than 10,000 years. Today, cannabis remains an understudied and underutilized resource, but United States legislation passed in 2014 and 2018 have re-energized cannabis crop development for medicinal, grain, and fiber applications.
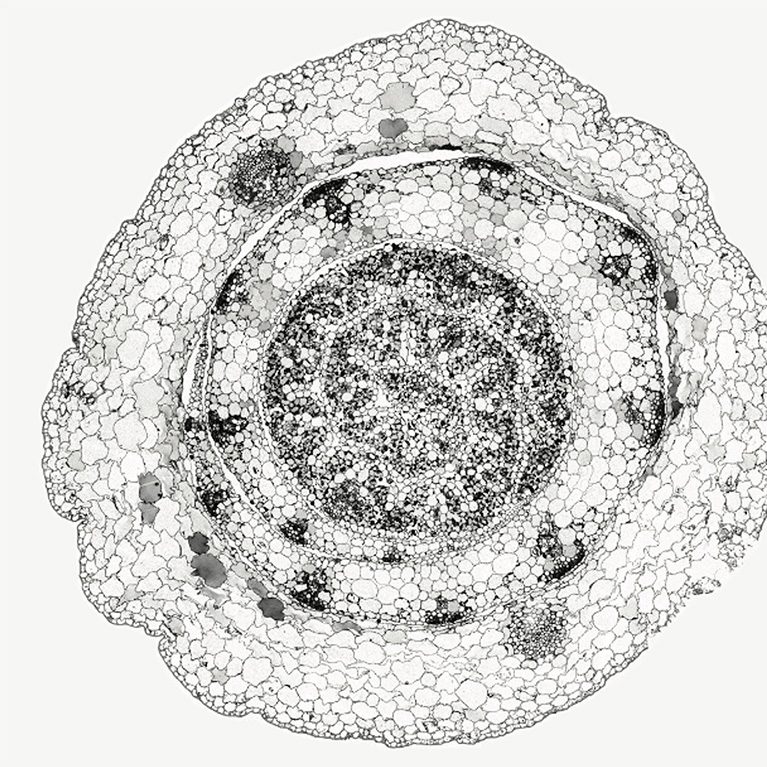
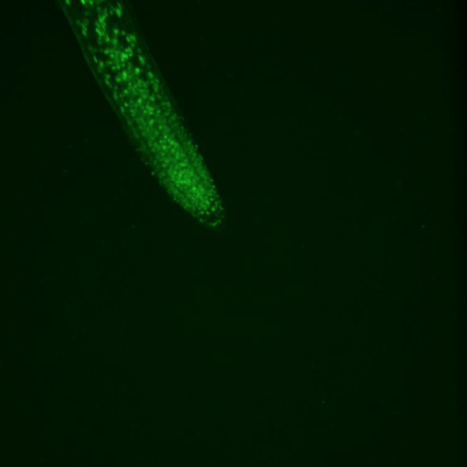
Two-in-one root armor protects plants from environmental stressors and fights climate change
LA JOLLA—Plants may burrow into the ground and stretch toward the sun, but they’re ultimately stuck where they sprout—at the mercy of environmental threats like temperature, drought, and microbial infection. To compensate for their inability to up and move when danger strikes, many plants have evolved ways to protect themselves by altering their physiology, such as building armor around parts of their body and roots called the periderm. However, since many plant biologists who study tissue development look at young plants, later-in-life periderm development has remained relatively unexplored.
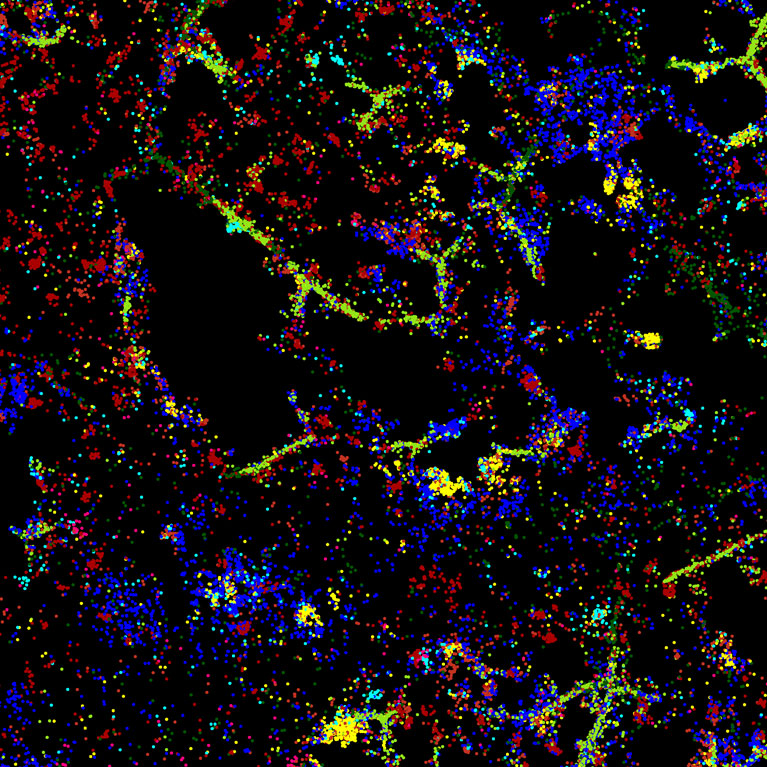
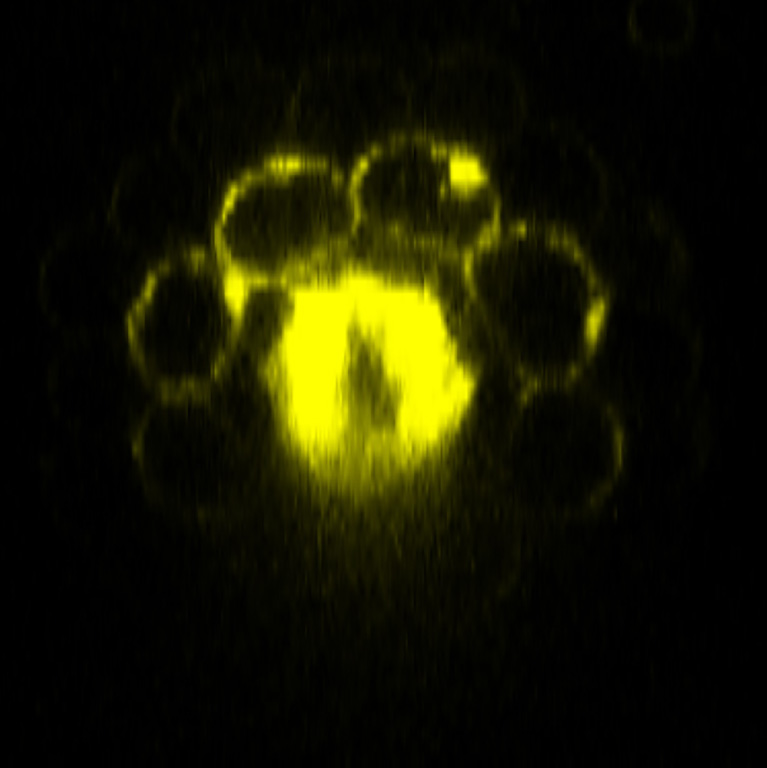
Plant cells gain immune capabilities when it’s time to fight disease
LA JOLLA—Human bodies defend themselves using a diverse population of immune cells that circulate from one organ to another, responding to everything from cuts to colds to cancer. But plants don’t have this luxury. Because plant cells are immobile, each individual cell is forced to manage its own immunity in addition to its many other responsibilities, like turning sunlight into energy or using that energy to grow. How these multitasking cells accomplish it all—detecting threats, communicating those threats, and responding effectively—has remained unclear.
Superior photosynthesis abilities of some plants could hold key to climate-resilient crops
LA JOLLA—More than 3 billion years ago, on an Earth entirely covered with water, photosynthesis first evolved in little ancient bacteria. In the following many millions of years, those bacteria evolved into plants, optimizing themselves along the way for various environmental changes. This evolution was punctuated around 30 million years ago with the emergence of a newer, better way to photosynthesize. While plants like rice continued using an old form of photosynthesis known as C3, others like corn and sorghum developed a newer and more efficient version called C4.
Seven Salk scientists named among most highly cited researchers in the world
LA JOLLA—Salk Professors Joseph Ecker, Ronald Evans, Rusty Gage, Satchidananda Panda, Reuben Shaw, and Kay Tye, as well as research assistant Joseph Nery, have all been named to the Highly Cited Researchers list by Clarivate. The 2024 list includes 6,636 researchers from 59 countries who have demonstrated “significant and broad influence in their fields of research,” as reflected by their publication of multiple papers over the past decade that rank in the top 1% by citations for their fields.
Joanne Chory, Salk Institute professor and pioneering plant biologist, dies at age 69
LA JOLLA—Salk Professor Joanne Chory, one of the world’s preeminent plant biologists who led the charge to mitigate climate change with plant-based solutions, died on November 12, 2024, at the age of 69 due to complications from Parkinson’s disease. She was diagnosed with Parkinson’s in 2004 and, despite the challenges, continued to lead her research team until the time of her death.
Scientists create first map of DNA modification in the developing human brain
LA JOLLA—A new study has provided an unprecedented look at how gene regulation evolves during human brain development, showing how the 3D structure of chromatin—DNA and proteins—plays a critical role. This work offers new insights into how early brain development shapes lifelong mental health.
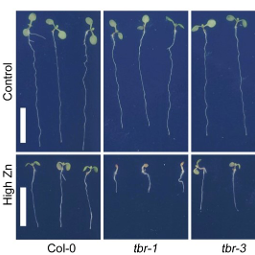
Study reveals key gene protecting plants from harmful metals in soil
LA JOLLA—The negative impact of human activity on Earth doesn’t just affect our planet’s atmosphere—it goes much deeper, into its soils. For instance, excessive application of manure or sewage sludge can increase heavy metal concentrations in agricultural land where vital crops are grown. One of these heavy metals is zinc, a micronutrient necessary for plant and animal health. In excess, however, zinc can be extremely damaging to sensitive plant species.
Salk Professor Joanne Chory named 2024 Wolf Prize Laureate in Agriculture
LA JOLLA—Salk Institute Professor Joanne Chory has been selected by the Wolf Foundation to receive a 2024 Wolf Prize in the field of agriculture for her “key discoveries on plant developmental biology of relevance for crop improvements.” The award is endowed annually to scientists and artists worldwide for their “outstanding achievements in advancing science and the arts for the betterment of humanity.”
Key nutrients help plants beat the heat
LA JOLLA—Global temperatures are on the rise, with experts projecting an increase of 2.7°F by 2050. Because plants cannot regulate their own temperatures, they are especially sensitive to these temperature changes. In higher temperatures, plants instruct their root systems to grow faster, creating long roots that stretch through the soil to absorb more water and nutrients. While this response may help the plants in the short term, new research suggests it’s both unsustainable for the plants and potentially harmful for humans in the long term.
Artificial intelligence helps scientists engineer plants to fight climate change
LA JOLLA—The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) declared that removing carbon from the atmosphere is now essential to fighting climate change and limiting global temperature rise. To support these efforts, Salk scientists are harnessing plants’ natural ability to draw carbon dioxide out of the air by optimizing their root systems to store more carbon for a longer period of time.
Controlling root growth direction could help save crops and mitigate climate change
LA JOLLA—Above ground, plants stretch toward the sun. Below ground, plants tunnel through the earth. As roots soak up water and nutrients from surrounding soil, they grow and stretch to develop distinct root system architectures. The root system architecture determines whether roots remain in the shallow soil layers or grow steeper and reach deeper soil layers. Root systems are central to plant survival and productivity, determining the plant’s access to nutrients and water and, therefore, the plant’s ability to withstand nutrient depletion and extreme weather like drought.
Salk Professor Joanne Chory honored with Benjamin Franklin Medal in Life Science
LA JOLLA—Salk Institute Professor Joanne Chory has been selected by the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia to receive a Benjamin Franklin Medal in Life Science for her achievements in plant science. She will receive a 14-karat gold medal and a $10,000 honorarium at the Franklin Institute Awards Ceremony in April 2024. Chory joins other extraordinary scientists and engineers as a Franklin laureate, including Nikola Tesla, Marie and Pierre Curie, Thomas Edison, Albert Einstein, and Jane Goodall, among others.
Iron influences plant immunity and may promote resiliency against climate change
LA JOLLA—Plants and animals alike rely on iron for growth and regulation of microbiomes—collections of bacteria, fungi, and more that co-exist in places like the human gut or the soil around a plant’s roots. Plants face a special challenge when acquiring iron, since the strategies plants use to increase iron availability alter the root microbiome and can inadvertently benefit harmful soil-dwelling bacteria.
Salk teams assemble first full epigenomic cell atlas of the mouse brain
LA JOLLA—Salk Institute researchers, as part of a worldwide initiative to revolutionize scientists’ understanding of the brain, analyzed more than 2 million brain cells from mice to assemble the most complete atlas ever of the mouse brain. Their work, published December 13, 2023 in a special issue of Nature, not only details the thousands of cell types present in the brain but also how those cells connect and the genes and regulatory programs that are active in each cell.
Seven Salk scientists named among best and most highly cited researchers in the world
LA JOLLA—Salk Professors Joseph Ecker, Ronald Evans, Satchidananda Panda, Rusty Gage, and Kay Tye, as well as Assistant Professor Jesse Dixon, have been named to the Highly Cited Researchers list by Clarivate. The 2023 list includes 6,849 researchers from 67 countries, all of whom demonstrate “significant and broad influence reflected in their publication of multiple highly cited papers over the last decade.” This is the ninth consecutive year that Ecker and Gage have made the list. Joseph Nery, a research assistant II in the Ecker lab, was also included on the list.
“A new era in brain science”: Salk researchers unveil human brain cell atlas
LA JOLLA—Salk Institute researchers, as part of a larger collaboration with research teams around the world, analyzed more than half a million brain cells from three human brains to assemble an atlas of hundreds of cell types that make up a human brain in unprecedented detail.
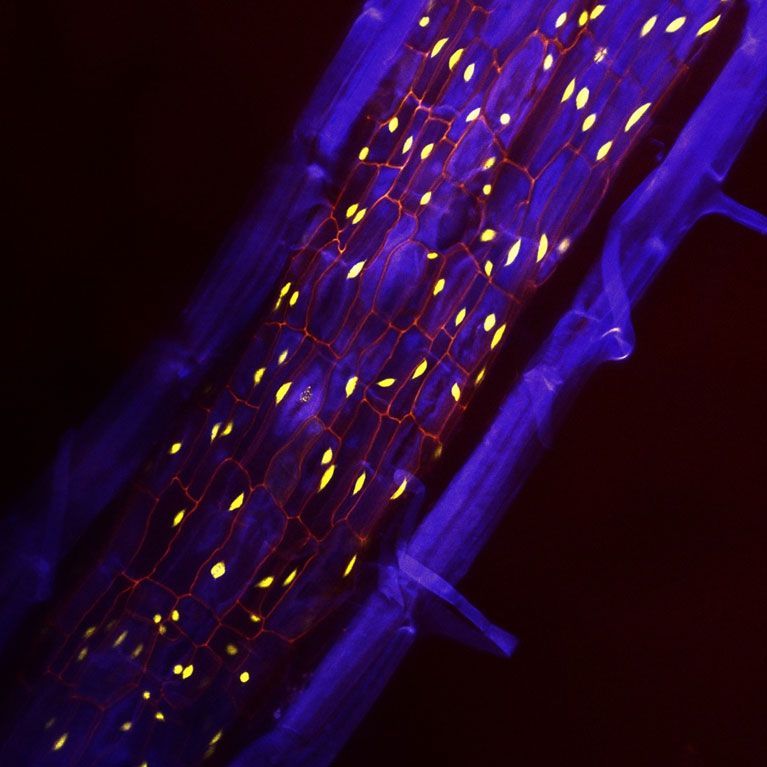
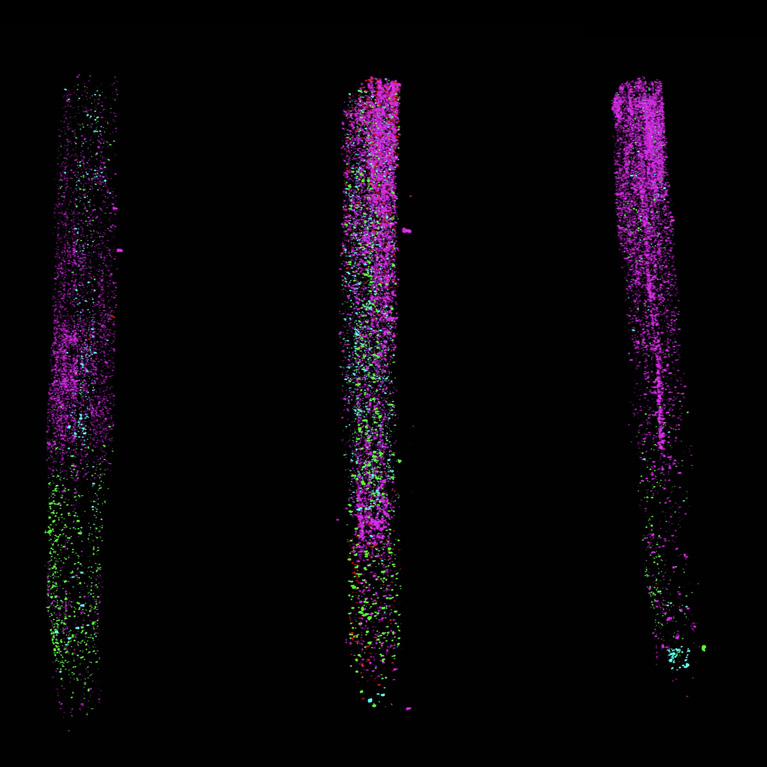
Seeing the insides of plants in 3D
LA JOLLA—The cellular life inside a plant is as vibrant as the blossom. In each plant tissue—from root tip to leaf tip—there are hundreds of cell types that relay information about functional needs and environmental changes. Now, a new technology developed by Salk scientists can capture this internal plant world at an unprecedented resolution, opening the door for understanding how plants respond to a changing climate and leading to more resilient crops.
Salk Institute receives $50 million from Hess Corporation to mitigate climate change through plant science
LA JOLLA—Hess Corporation is donating $50 million to the Salk Institute’s Campaign for Discovery: The Power of Science, a seven-year, $750 million comprehensive fundraising campaign to attract the people and build the technology and space necessary to accelerate critical research. This gift will specifically advance Salk’s Harnessing Plants Initiative—an effort to mitigate climate change by optimizing plants and supporting wetlands to increase capture of excess atmospheric carbon—and provide vital infrastructure for this work by establishing the new Hess Center for Plant Science.